Meda'in Saleh - Introduction:
This Nabataean city is located in Saudi Arabia, approximately 320 kilometers south of Petra. This Nabataean city has 131 tombs spread out over 13.4 kilometers. The city proper as a siq, walls, towers, …
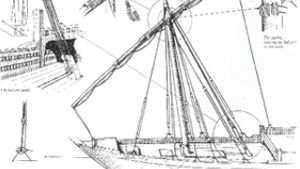
History and Construction of the Dhow:
Text copyright Canbooks Pictures copyright held by their respective owners
Picture by Marion Kaplan Used with permission
Picture by Marion Kaplan Used with permission
For many centuries, boats …
Who were the Nabataeans?:
At its peak, Nabataean influence stretched from modern day Yemen to Damascus, and from western Iraq into the Sinai Desert—at least according to some historians. We cannot be sure how large the area of …
Nabataean Culture:
When one uses the word ‘culture,’ it can encompass many different subjects. In this page, we want to look at a number of topics, such as Nabataean houses, ceramics, and water collection …
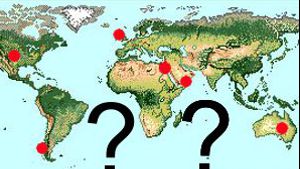
Who were the ancient Arab Sea Traders?:
Historians tell us that throughout history Arabs have conducted trade between the ancient European kingdoms and Asia. Most ancient historians were content to simply call these traders …
Who were the Ancient Arab Sea Traders?:
Historians tell us that throughout history Arabs have conducted trade between the ancient European kingdoms and Asia. Most ancient historians were content to simply call these traders …
Desert Life:
For thousands of years, the people of the Middle East have been moving from nomadic lifestyle to settled lifestyle. Cities offer better protection and are centers for learning and exchanging ideas. …
Talking with Dan Gibson #02 The Nabataeans, Builders of Petra:
Series: Talking with Dan Gibson: A review of Dan Gibson’s book: The Nabataeans, Builders of Petra. This is a look at the Arab merchant empire in Arabia before the time of Muhammad, who was …
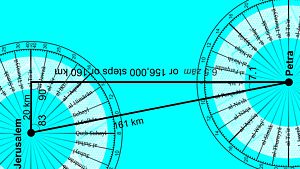
How Far did the Ancient Nabataean Merchants Travel?:
How Far did the Ancient Nabataean Merchants Travel?
Around 287 BC Ptolemy II of Alexandria in Egypt set in motion a plan that would change the ancient world. Abandoning the life of military conquests …
The 12 Tribes of Ishmael:
Many of us are familiar with the ancient story of Abraham and his desire to have a son. In the Biblical account of his story, Abraham first had a son with his ‘handmaiden’ Hagar. This first-born son …
The Price of Honor:
Sixth, because they were misunderstood, they may have felt freer to use deception and bribery. Again, a parallel can be made with the gypsies of modern Jordan. Because of their low social status, they …
Ancient Sailing Techniques:
Text copyright Canbooks.
Picture copyright is held by their perspective owners
Introduction
In this short paper I would like to outline the basic skills that were necessary for sailing in ancient …
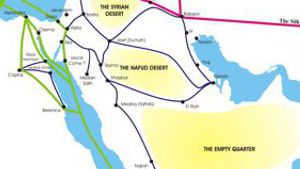
Nabataean Trade Routes:
Many historians have puzzled over the early trade routes of the Nabataeans. Since there were no distinctive Nabataean cities at this time, most discussion on this topic disintegrates into vague …
Araq Al Amir in Wadi Sier:
Josephus writes in Antiquities of the Jews, (12,IV,II) that a certain Hyrcanus, in the time of Seleucus IV(187-175 BC) built a strong building of white stone, surrounded by a fine park and lake. On …
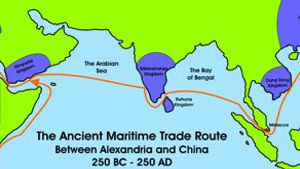
The Ancient Maritime Sea Route:
The Ancient Maritime Sea Route: 250 BC - 250 AD
During the period between 250 BC and 250 AD, a maritime sea route existed between Alexandra in Northern Africa and China. As trade took place along this …
Navigation and the Qibla #4 Further Information:
Click below to watch the video:
Additional information: Multiple windroses, water collection, Yemen, using ships, missing information
Transcript
Hello I am Dan Gibson, and welcome to the fourth …
Coins:
Ten typical Nabataean coins.
The Wall:
Sometime back in history, someone living in this same area as the Nabataean Inner Kingdom decided to do something about the desert raids. Their solution was brilliant. Forts were constructed on …
Parallel Maritime Histories:
(Greece, Egypt, India, South Yemen, China, Rome)
A number of things made the Nabataeans distinctive from other tribes in Arabia. One of them was their ability as seamen. Where did they learn their …
"Arabia" in Ancient History:
A discussion of the term ‘Arabia” and what it might have meant to Greek and Roman audiences
Throughout history, the Arabian Peninsula has been traditionally called ‘Arabia.’ This was …
Philadelphia (Amman):
The Roman city of Philadelphia (Amman)
This site has been occupied since 300 BC, but the early city of Ramoth-Ammon, the capital of the Ammonite civilization existed only from 1200 BC. The city was …
Gibson Answers Dr. King #5:
Video 5 of 6 videos addressing Dr. King’s paper: The Petra Fallacy. Dr. King chooses six mosques that he believes illustrate his theory of archaeoastronomy. Gibson then examines what history …
Pottery:
NABATAEAN POTTERY
A Nabataean oil lamp. Thousands of these have been discovered throughout Nabataea. Oil was poured into the middle of the lamp, and a wick was inserted in the left side and lighted. …
The Negev Wall:
A WALL IN THE NEGEV
Pictures copyright 2003 Arieh Bar-Lev
This wall is known as the K-Line and it is located between Mt. Ramon in the central Negev (100 km south from Beer-Sheva) and Mt. Romem. The …
Alexandria, Center of Trade:
The ancient city of Alexandria was founded in 332-331 BC by Alexander the Great. From it’s inception it was intended to be an important port for Egypt, for it would serve as a link between Egypt …
Gerasa (Jerash):
The Roman city of Gerasa (Jerash in Jordan)
In ancient times the area of Jerash was known as Gerasa. It is located on the banks of the river Chrysorhoas, about 42 km north of modern Amman Jordan. The …
The Stone Cutter:
The Stone Cutter by Brock Meier
A doomed quest of love and ambition, awash in the glories of the Nabataean Kingdom— The young sculptor Nahor enters the fast-track of the art world in the spectacular …
Nabataeans in Africa:
First Egyptian Connection
The city of Alexandria was established by Alexander the Great, and it quickly became a very important center for grain and other trade. As Alexandria gained importance as a …
Writing:
Introduction
As far as we know, the Nabataeans were not great writers of books. Very little literature has passed down to us. We have no literature from the early years, and the famous Petra Scrolls …
Nabataeans on the Mediterranean:
Nabataeans on Rhodes
Nelson Glueck mentions in his book Rivers in the Desert, page 197 that a Graeco-Nabataean inscription was discovered on the island of Rhodes. This book was printed in 1968.
During …
Roman Roads:
Fallen Roman Milestone along the Roman road known as the Via Traiana.
Part of the Via Traiana still in existence in south Jordan
Nabataeans in India:
The Indian Sub-continent was the natural meeting place for Arab, Indian and Chinese maritime merchants. The Malabar Coast on the west of India and the Chola Coast on the east witnessed a great …
Multi-Alphabet Theory:
Two Families of Alphabets
Throughout the Middle East, graffiti is found in a number of different forms, but they seem to fall into two distinct families of alphabets. These are important, for …
The Cave of Letters:
In 1951 a set of Nabataean manuscripts surfaced in the Middle East. They were purportedly from Wadi Sayaal, on the west side of the Dead Sea. The manuscripts included some twenty items, Some of them …
Bosra, Syria:
Bostra was the northern capital of the Nabataeans, located in southern Syria at the northern end of the Via Nova Traiana roadway.
When the Romans annexed the Nabataean Empire, Bostra became the …
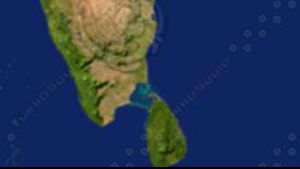
Nabataeans and Sri Lanka:
The Kingdom of Ruhuna
Godavaya is located on the coast of Sri Lanka. Here Sri Lankan and German archaeologists excavate the old Kingdom of Ruhuna, gathering evidence of its glorious past. Excavations …
Mukawir Fortress:
Mukawir is a fortress set on a high hill near the Dead Sea. It is the site of one of Herod’s palaces, and has the tradition of being where Salome danced and John the Baptist was beheaded. From …
Gadara (Um Qais):
The Roman city of Gadara
Gadara was a Roman town in the north of Jordan. It had a university from which Meleager, the great poet came. Today two theaters survive, plus several temples and piles of …
Southern Arabia:
Traditionally the Nabataeans have been known for their role in the incense trade. Frankincense and myrrh, the main components of the incense trade, were obtained from trees located in the southern …
The Petra Scrolls:
These scrolls consist of 152 rolls of burnt papyri found in the old Byzantine church in Petra. At first archeologists were very pessimistic about the Petra Scrolls. They were deep black, fragile, and …
Marib Dam:
The Marib Dam
As the Sabaean kingdom developed, they built a huge earth filled dam in the second half of the 6th century BC to hold back some of the water that came down the wadi. From the lake that …
Gods and Worship:
NABATAEAN PANTHEON
Stone Block God from Petra
Artistic rendering of Block God
Stone Block Gods
In the Greco-Roman world as well as the Parthian East, people have always accorded the gods with …
Tall Tales told by the Nabataeans:
As storytellers and liars, the Nabataeans ranked among the greatest. Many of their stories were believed by outside civilizations, and even to this day many people believe that the city of Petra is …
Humeima:
Copyright 2002 CanBooks
The Nabataean city of Humeima (ancient Hawara) an important historical site, as it is a city that was founded by the Nabataeans, and survived only into the Byzantine era. …
Nabataeans in China:
Chinese Texts
Through out Chinese history, Chinese explorers, ambassadors, and merchants made occasional trips to the western world. Many of their reports were written down. The Chinese text, however, …
Humeima Tombs:
Mosque Name: Humeima Tombs
Country: Jordan
City: Humeima
Year of construction (AH): 93 AD
Year of construction (AD): 712
GPS: 29.949629 35.34612
Gibson Classification: Between
Rebuilt facing Mecca: …
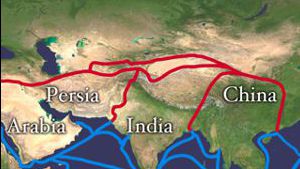
Spice Route Time Chart:
The Spice Route Time Chart Includes China, India, Arabia, Europe Best viewed on a wider screen.
Date Europe Arabia India, Ceylon, Central Asia China and the Far East 3000 BC - 0 BC …
Meda'in Saleh - Tombs:
Meda’in Saleh has 131 tombs spread out over 13.4 kilometers. The city proper as a siq, walls, towers, water conduits, and cisterns. We are trying to collect pictures, maps and other descriptions …
Meda'in Saleh - Tomb Decorations:
Special thanks to John and Kathy Haberman for all the photos on this page. Their contributions have greatly aided us in recording Meda’in Saleh for those who cannot enter Saudi Arabia at this …
Meda'in Saleh - Niches, Altars and God Blocks:
Special thanks to John and Kathy Haberman for all the photos below this point. Their contributions have greatly aided us in recording Meda’in Saleh for those who cannot enter Saudi Arabia at …
Meda'in Saleh - Tomb Database:
Archeologists have numbered each of the tombs in Meda’in Saleh. There are over 130 tombs or monumental buildings. On this page we have tried to match up photos supplied by our viewers with the …
Burial Practices:
NABATAEAN BURIAL PRACTICES
Every day hundreds of tourists stare in awe at the magnificent tombs in the ancient city of Petra. Indeed, they are among the most fantastic tomb facades in the world. But …
The Ptolemies of Egypt:
The Nabataean people began emerging from the Arabian Desert about the same time that Ptolemy I Soter became the ruler of Egypt. At first these emerging civilizations clashed with one another, but …
South Forts:
View from the Naqab Escarpment near the Naqab fort
East of Naqab
Naqab Fort
(Location: N 29 degrees, 59.863, E 035 degrees 30.281, Elevation 5495 feet)
Just east of the old highway, in the village …
An Overview of Chinese History:
15th Century BC to 15th Century AD
A brief historical overview to help students of Nabataean history understand what was taking place in other parts of the world, and how these changes affected …
Nabataean Zodiac:
NABATAEAN ZODIAC
Artifacts found among the ruins of a Nabataean temple, known as Khirbet Tannur have contributed to our knowledge of the art and religion of the ancient Nabataeans. At the same time, …
Trade on the Red Sea:
250 BC - 250 AD
During the period between 250 BC and 250 AD, a maritime sea route existed between Alexandra in Northern Africa and China. As trade took place along this route, a number of kingdoms …
The Elephant and the Nabataeans:
Why did the desert dwelling Nabataeans have such a close association with elephants? Why did these beasts decorate their public buildings? And were they Indian, Syrian, North African, or African …
Cane (Qana'):
Cane (Qana) was the southern most port in South Arabia. The incense fields, and the heartland of Yemen were to the north of this port. Incense was loaded onto dhows here for destinations in Europe via …
Making Sense of Middle Eastern Religions:
MAKING SENSE OF MIDDLE EASTERN RELIGIONS
Copyright 2003 CanBooks
Throughout the ancient Middle East, various religions and forms of worship sprang up or evolved at different times. Many of these are …
Aden:
The ancient city of Aden is located at the south west corner of Yemen. It was built at the base of a volcano that rises up to 300 metes from sea level. The old port was built in the back of the bay …
The Camel and the Nabataeans:
For centuries the Nabataeans moved goods in the desert by camel caravan. The camel was the backbone of their merchant enterprise, and it is only through understanding the camel, that we can better …
Muza (Al Mokha):
The port of al Mokha has been in use since ancient time. However, once the maritime incense route was established, this port became a busy center of trade. Once the Nabataean Empire was handed over to …
Dong Song Kingdom in Vietnam:
Funan Kingdom in Vietnam 250 BC - 250 AD
During the period between 250 BC and 250 AD, a maritime sea route existed between Alexandra in Northern Africa and China. As trade took place along this route, …
Berenice:
Around 275 BC, Ptolemy II (Philadelphos), king of Egypt, founded a port on the Red Sea coast. He named it after his mother, Berenike I. This port was originally created to aid in the importation of …
King really hates Gibson! - Qibla Controversy Ep.10:
Archaeology and Islam #20 - Hud and Salih:
Click below to watch the video:
Who were the prophets Hud and Salih? Where do they fit in history and geography? Why did they make Muhammad’s hair turn grey?
Transcript Video #20 *This is …
Travel the Incense Route from Ubar to Gaza:
Incense was located in Yemen in what is known as the Hadramout area, and also in Oman along the shores south of Ubar. To get the incense, Nabataean merchants traveled to Yemen and Oman, and then …
Myos Hormos:
For many years the location of the northern Egyptian port on the Red Sea was unknown. Ancient historians like Strabo and the writer of The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea’ gave us know clue to …
Nessana:
A Nabataean city in the Negev
Nabataeans in Antarctica?:
It has been suggested by some of our readers, that the Nabataeans may have reached Antarctica, and even South America. This amazing claim is based on a theory that revolves around Piri Re’is map …
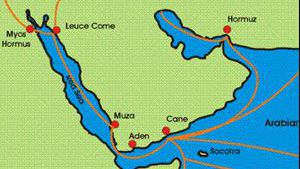
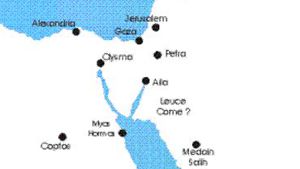
Leuce Come:
The Nabataeans maintained two ports that we know about. The first was Aila at the northern end of the Gulf of Aqaba. The Nabataeans also maintained a port on the Red Sea known as Leuce Come (meaning …
Aila Port (Ayla) (Aqaba):
The Nabataeans maintained a port at Aila at the northern end of the Gulf of Aqaba. This port was used almost exclusively by Arab ships as the Gulf of Aqaba was known for its foul winds, making it a …
Water Collection:
The Nabataeans greatest accomplishment was probably their system of water management. They developed a system to collect rainwater using water channels, pipes, and underground cisterns. Added to this, …
Hawara (Humeima):
The Nabataean city of Hawara (modern Humeima) is an important historical site, as it is a city that was founded by the Nabataeans, and survived only into the Byzantine era. During the Muslim …
Ayl:
Ayl was a major stopping center for camel caravans in the Edomite highlands. Here there was water and fodder.
Special thanks to Fawzi Abudanh for this great picture taken on November 2003. Fawzi was …
Sela:
Sela is one of the first places that the Nabataeans appear, long before they settled into the area that was to become Nabataea. The mountain of Sela suited them well, for Sela is a small mountain with …
Sobota (Shivta):
Sobota was a Nabataean agricultural city in the Negev. A ring of houses faced inwards, providing protection.The city had churches and a temple.
Obodat (Avdat):
This ancient caravan station evolved into a large desert city known as Obodat (after a Nabataean king). It was first founded as a road station in the 3rd century BC where two trade routes converged. …
Gaza (Jenysos) (Roman Teda):
Gaza is one of the older cities in the world. The city is strategically situated between two continents, Asia and Africa. This geographical location made the city acquire a strategic and extraordinary …
Elusa (Haluza):
This Nabataean city can only be reached with a four-wheel drive. It is covered in sand, but has a very impressive church, theater, and inscriptions. In the 5th century it was surrounded by vinyards …
PETRA: Walk In:
Arriving in Petra
Petra is located in the country of Jordan in the Middle East. Tourist visas are easy to obtain, and travel to Jordan is usually quite cheap. Once you get to Jordan, local transport …
PETRA: The Siq (Thaniya):
A “thaniya” is a small crack in a mountain. The city of Petra had several thaniyas, or passages through the mountain. The main one is known as the “siq” alowing people to pass …
PETRA: The Small Siq (Thaniya):
As mentioned, there are two main thaniyas, or siqs into Petra. There is also a third, much less know thaniya, that is a great experience. However, this is quite a scamble and should only be done by …
PETRA: Treasury:
As one comes to the end of the siq, the first, and greatest monument of Petra slowly comes into view. This is the famous Treasury monument. It is probably a good idea to stop here and take a picture. …
PETRA: Restoration in the Desert:
Repair Work among the Monuments of Petra, in Jordan
The Illustrated London News, March 31, 1962, Page 502⁄503
Archeological Section no 2085
Used by permission
In a poor country with a rich …
PETRA: Mystery of the Treasury Monument:
In 1812 the Swiss geographer and scholar, Johannes L. Burckhardt discovered Petra and stood amazed at the magnificence of the Treasury Monument. Since that time thousands of tourists have stood amazed …
PETRA: The Treasury Plaza:
The Treasury Monument in Petra has always been a mystery. No one was sure when the monument was built, nor exactly what its purpose was, although we present an argument on this website that it was the …
PETRA: Street of Facades:
After the viewing the Treasury, we come next to the Street of Facades, which is lined with tall, impressive tombs, with large facades or false faces on their fronts.
The street of facades eventually …
PETRA: Water Works:
Along the left hand side of the siq, a covered water channel used to bring water from the spring in Wadi Musa into the center of Petra.
Along the right hand side of the siq, clay water pipes …
PETRA: Theater:
The next main monument as we pass along the road into the heart of the city of Petra is the theater up ahead on our left.
Petra's theater is cut out of solid rock, and badly deteriorated. The …
PETRA: The Royal Tombs:
The first of the so called Royal Tombs is the Urn Tomb. This tomb is built high on the mountain side, and requires climbing up a number of flights of stairs. Abbe' Starcky has suggested that this …
PETRA: High Place:
also known as Robinson’s High Place
The High Place is located at the very top of a mountain. If you want to see it, you will have to climb up there.
The main steps to the high place …
PETRA: The Colonnade Street:
The Colonnade Street runs through the center of Petra, with many excavated and unexcavated sites on either side.
PETRA: The Great Temple:
(The Royal Courts?)
In 1921 an archeologist named Bachman published a survey of the city of Petra, which soon became a standard that was used by archeologists for several decades. On the south side …
PETRA: The Temple of Al Uzza:
(The Temple of the Winged Lions)
The American Expedition to Petra (Utah University) started work on this site in 1974 and excavated it until 2005. Dr. Philip Hammond headed up the excavation for much …
PETRA: The Temple of Dushares / Bint / Hubal:
(Qasr al Bint)
Qasr el-Bint, the temple of Dushares, has the largest facade in Petra — 4 m wider than the Khazneh and the Great Temple. It belongs to the Parthian ‘flight’ type of temples …
PETRA: The North Tombs:
The Tombs north of The Royal Tombs
The Tombs on this page are located along the side of Jebel el-Kubtha, and are found north of the Royal Tombs.
The Sextius Florenthinus Tomb, built for the Roman …
PETRA: The Deir (Monestary):
People in the door of the Deir The Deir monument is 40.2 meters wide and is carved deep into the side of the mountain. The door itself is 8 meters high. The main inside chamber is huge. It is 11.5 …
PETRA: Jebal Habis:
Jebal Habis is a small mountain that stands at the back of Petra. It is dwarfed by the huge shadow of Um al Biera behind it. Jebal Habis is an important mountain however, for along it’s bottom …
PETRA: Um el Beira:
Um el Beira (Biyara) is the great flat topped mountain in the back of Petra. It is possible to climb this mountain if you are good at hiking. Along the left side of the mountain is a processional way …
PETRA: Ancient Board Games:
At the Second Annual Conference for Nabataean Studies, Dr. Bilal Khrisat of the Hashemite University presented a paper that introduced the conference to the various board games that are found in …
PETRA: Rules for Ancient Games:
Rules and Links for the ancient game of Senet
Rules
The equipment for Senet is very simple:
There are 10 movers, each quite different from each other. In the traditional Egyptian game there were 5 …
PETRA: Southern Tombs:
Near the south end of Petra, close to the jinn rocks that mark the southern side of the Sacred Area are a series of tombs seldom visited by tourists.
In one tomb there are twelve graves cut into the …
PETRA: Al Sabra Suburb:
In Wadi Sabra, the Nabataeans had an agricultural and industrial settlement. Hewn into the cliff on the left is a theater. Above the theater was a water reservoir. Behind the theater stage is another …
PETRA: City Walls:
Contrary to popular opinion, Petra is not a city hidden in a crack in a rock mountain. That describes the Treasury monument, but not Petra proper. The city of Petra is located in a wide open valley. …
PETRA: Al Beidha:
After Petra, Al Beidha or Little Petra is the next most important site for the casual visitor in Wadi Musa. This site is only a few kilometers from Petra and easily accessible by taxi or rented car. …
PETRA: Al Beidha (The Neolithic Village):
Outside of Beidha one can find the remains of a Neolithic village. This village has been excavated and is open for the public to see. This is a very ancient site that predates Petra and Al Beidha. It …
PETRA: Churches:
The Christian era at Petra came during the 3rd, 4th and 5th centuries, when the area came under Byzantine control. Although the city remained mainly pagan, there were three churches and a cathedral of …
PETRA: Kubtha High Place:
In recent years the Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities in Jordan has repaired the stairs to Al Kubtha Mountain, making it possible for tourists to climb to the top and visit the High Place and other …
PETRA: Small Delights:
A selection of small things to see around Petra. Most of these are beytel or alters. If you visit Petra, see how many of these you can spot on your visit.
Can you see the crescent …
PETRA: The Bedul:
The Bedul are a small tribe of Bedouin who used to live in the caves in Petra. The Jordanian government built them a small village north of Petra with schools and modern utilities. Below are some …
The Northern Desert Trek:
Crossing the trackless desert can be a life-threatening experience, if you do not know any sources of water. The ancient Nabataeans created routes through the desert by creating their own watering …
Dedan:
Ancient Dedan is known as Al Ula today. In the ruins of the old city there are inscriptions that indicate the Dedanites were preceded by a Minean settlement. The Mineans established a center at this …
Petroglyphs:
It has been assumed by archeologists and historians that the petroglypth method of writing and communication preceded writing in general, and that once writing systems were developed that the use of …
Najran:
Najran was an important stopping place on the Incense Road. It is located in the southern part of Saudi Arabia. The oasis of Najran has been inhabited for about 4,000 years. Najran’s most …
The Southern Desert Trek:
South of Medina the incense caravans took several different routs. Some traveled through the rugged mountains, while others kept closer to the desert to avoid inhabited places where thieves or taxes …
Flora & Fauna of Nabataea:
This web age will cover the Flora and Fauna found in the deserts of southern Jordan and northern Saudi Arabia (Nabataea).
The Wild Plants of Jordan, their Medical, Perfume and preventative Qualities, …
Humeima Abbas House:
Mosque Name: Humeima Abbas House
Country: Jordan
City: Humeima
Year of construction (AH): 80 AD
Year of construction (AD): 699
GPS: 29°56’59.64”N 35°20’45.33”E
Gibson …